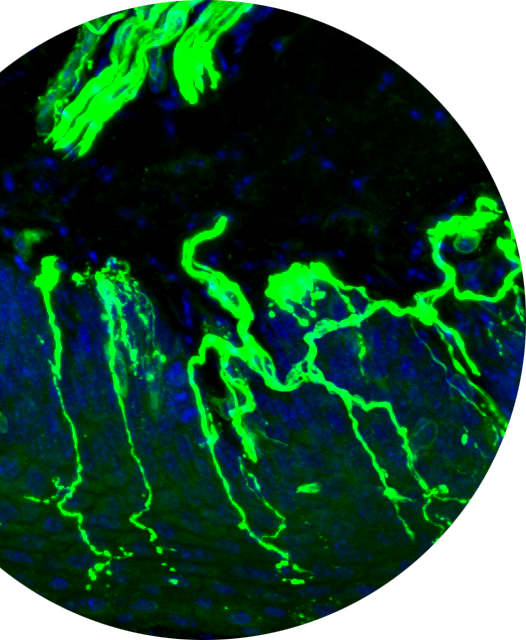
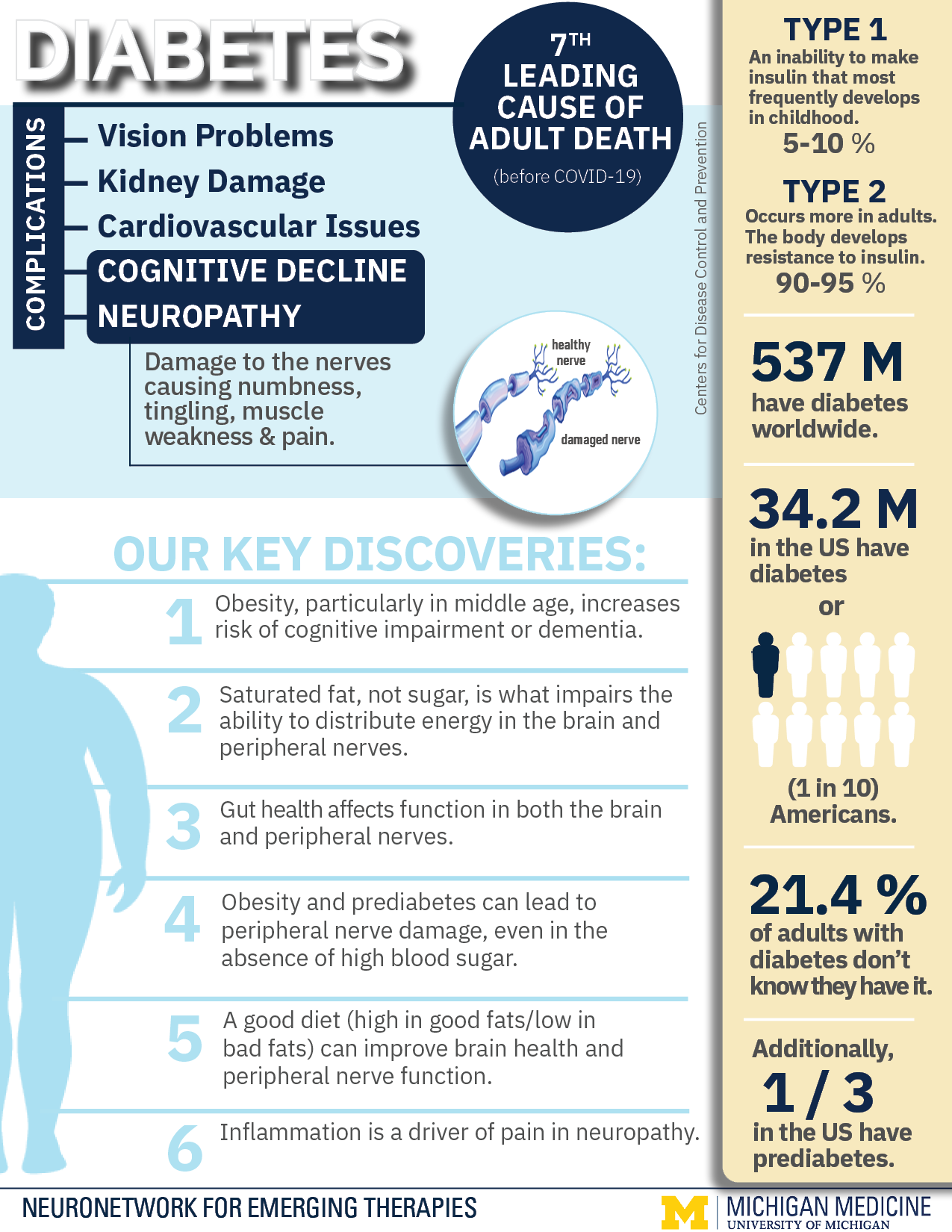
Diabetes is a global epidemic and public health burden. Almost 537 million adults are living with diabetes worldwide, a number projected to increase to 784 million by 2045. In the United States, 1 in every 10 adults have diabetes, and over 20% of those don’t even know they have it.
- Type 1 diabetes (T1D) can develop at any age, but most frequently is diagnosed in adolescents and children. In T1D, the pancreas loses the cells that make insulin, the glucose regulating biomolecule.
- Type 2 diabetes (T2D), the more common form, accounts for around 95% of diabetes cases and is diagnosed most frequently in adults. In T2D, the body develops insulin resistance and can no longer regulate glucose. Unfortunately, controlling blood glucose alone is not sufficient to slow or reverse damage to complication-prone tissues, including peripheral nerves.